Announced at SAPPHIRE 2023, the Green Ledger or Green Book was further explained on October 19, 2023 by Stephan MÜLLER, Global Solution Owner for Finance & Risk at SAP, in a YouTube video The Path to Green Ledger – Discover how to Manage Sustainability with SAP
A year later, following a pilot customer trial, the solution is now available in General Availability (GA) for RISE and GROW customers.
Challenges
Faced with the urgency of climate action, companies are powerless to make the most pertinent decisions without a real vision of their impact. The Green Ledger makes it possible to track and measure carbon footprints on the basis of transactional data (fine-grained, not averaged values), and relate them to the usual Finance & Controlling allocation objects (G/L accounts, cost centers, profit centers), but with an evaluation in terms of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions expressed in tCO2e instead of traditional currency.
Methods
The Green Ledger relies on other solutions in the SAP Sustainability portfolio: SAP Sustainability Footprint Management (SFM) for fine-grained carbon footprint calculation at product level, SAP Sustainability Data Exchange (SDX) for carbon footprint exchange with suppliers, and SAP Sustainability Control Tower (SCT) for data consolidation.
As the company is often part of a hybrid system landscape, Green Ledger naturally relies on SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) and SAP Datasphere to harmonize data collection and presentation. In addition to actual values, budgeted values can also be tracked: SAC Planning (Integrated Financial Planning for SAP S/4HANA and S/4HANA Cloud) offers a ‘Greenhouse Gas Emission Planning’ scenario. The SAP Datasphere online help Green Ledger Reporting for SAP S/4HANA and SAP S/4HANA Cloud | SAP Help Portal shows the possibilities for tracking indicators and graphs.
The features
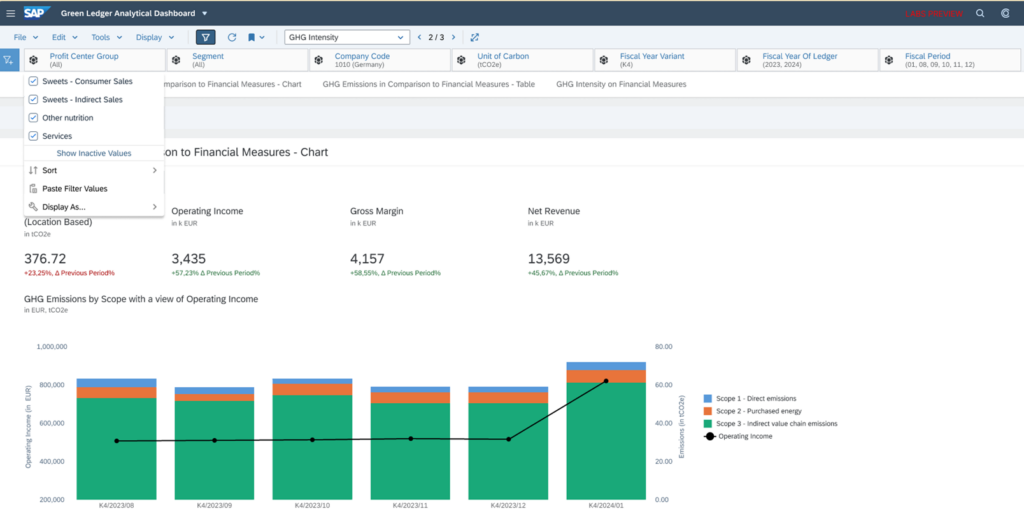
The Green Book dashboard links financial data with carbon data, displaying values at the required granularity.
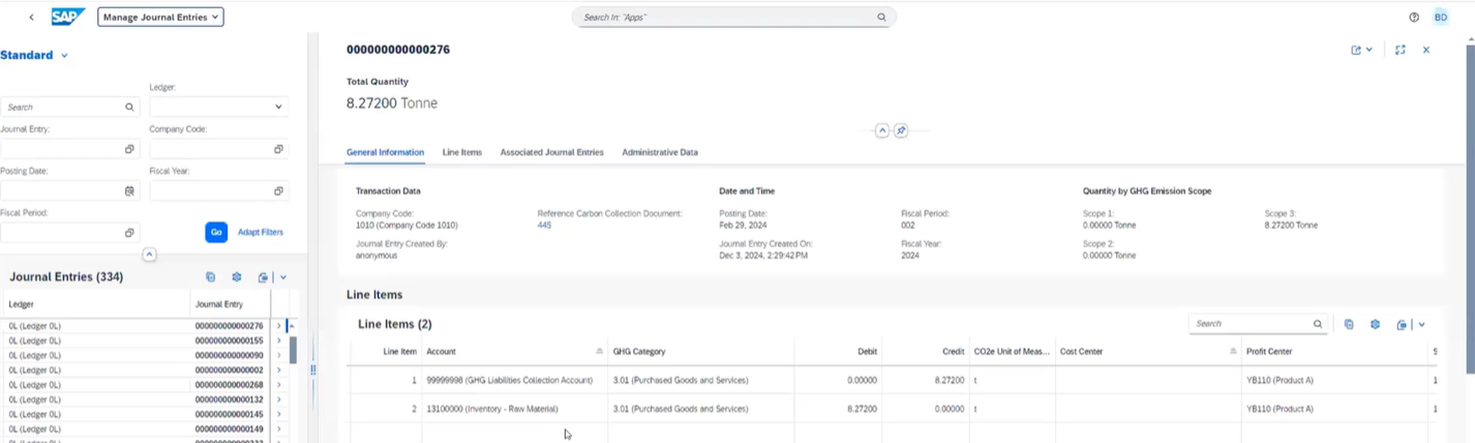
The Green Ledger works like a cost accounting system, expressed in CO2 equivalent weights. Carbon collection documents (imported from ERP item documents, CSV files or created manually) are recorded and generate debit/credit entries.
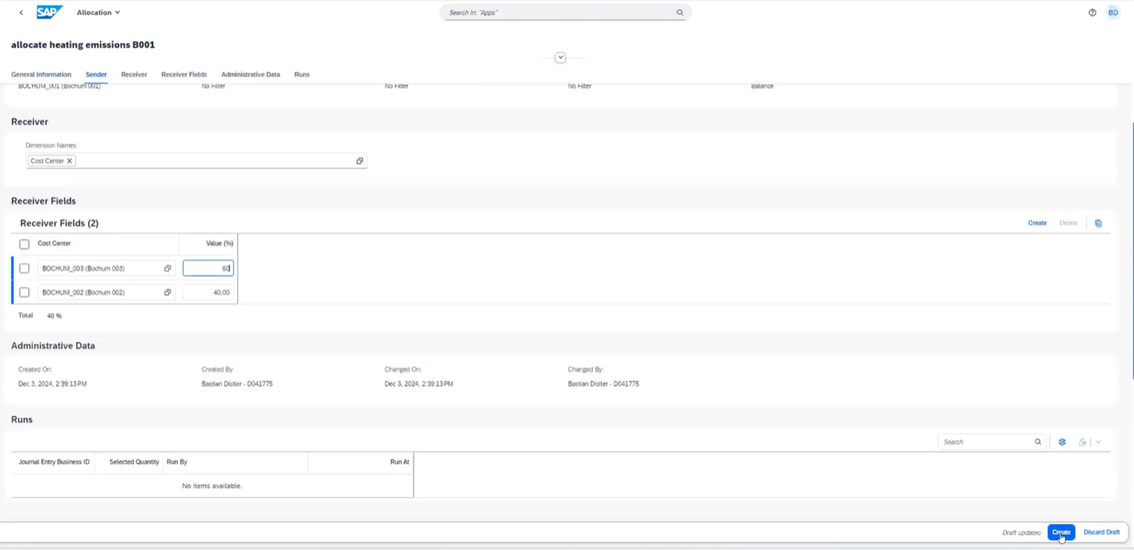
GHG emissions allocation documents are used to allocate scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions from emitters (departments that ” generate emissions on behalf of “) to recipients (departments that ” consume “).
To find out more
SAP has published a guide entitled “Financial or carbon accounting: the same level of accuracy. The road to a green ledger”, aimed in particular at CFOs.
By integrating financial and environmental data at the transactional level, reliability, accuracy, automation and regulatory compliance are enhanced. The Green Ledger gives companies an undeniable competitive edge, enabling them to manage their sustainability objectives more precisely, while adapting to change and maintaining their overall economic performance.
Laetitia VOGEL, Head of SAP Sustainability at Applium, will be happy to answer any questions you may have about our Applicum4Green offer.