The challenges of sustainability
Sustainability is the new frontier of digital transformation. The time to act is now: investors, regulators and consumers are increasingly demanding socially, environmentally and economically responsible products and services. Companies are looking to reduce GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions, reduce waste, increase circularity and use socially responsible business practices throughout the life cycle of products and value chains. The key challenge for the company is to keep both sustainability profitable and profitability sustainable.
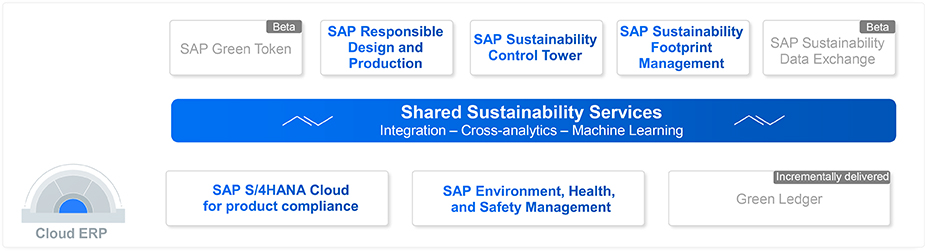
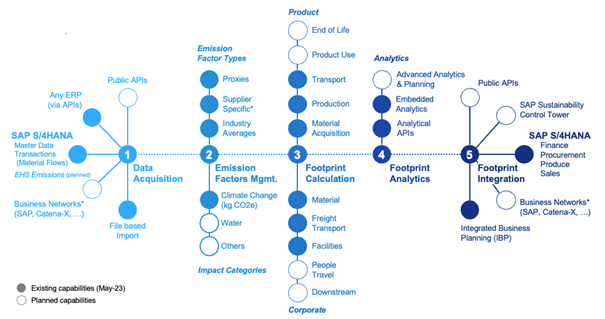
The SAP solutions shown in the diagram above correspond to the following functionalities:
SAP Sustainability Footprint Management
A solution based on existing ERP data in SAP systems, with possible connection to emissions databases, for calculating and managing carbon flows in scope 1, 2 and 3 GHG emissions for accurate, comprehensible emissions results.
SAP Sustainability Data Exchange :
An application for securely exchanging standardized sustainability data with 6 million companies across the SAP Business Network throughout the value chain using Partnership for Carbon Transparency (PACT) standards.
Green Ledger :
A project to combine financial and environmental data for better decision-making and insights directly into SAP S4/HANA Cloud ERP.
EHS EM (Environmental, Health, and Safety – Environmental Management) :
This module, already available on SAP ECC, ensures compliance with environmental regulations relating to emissions. EHS EM encompasses all aspects of environmental compliance, as well as the management of an organization’s impact on the environment, including air and water pollution, GHG emissions inventory and waste management. When SAP SFM is used with SAP EHS EM, SFM can retrieve regulatory data on carbon emissions and environmental material flows, such as water and waste, from EHS EM.
* To find out more about SAP Green Token: GreenToken by SAP (green-token.io). SAP Sustainability Data Exchange and Green Ledger will be covered in the paragraph on SAP Sustainability Footprint Management.
Among SAP’s Sustainability solutions, Applium has selected 3 for its Applium4Green offering: SAP Sustainability Control Tower (SCT), SAP Sustainability Footprint Management (SFM) and SAP Responsible Design and Production (RDP).
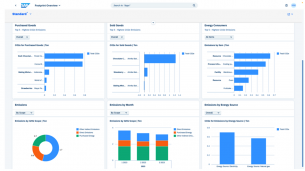
Piloting and holistic sustainability reporting with SAP Sustainability Control Tower (SCT) :
The CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), an EU directive that will enter French law in December 2023, defines the rules under which European companies must publish their sustainability-related information. A progressive timetable including more and more companies has been established for the publication requirements according to the following criteria :
Published for the fiscal year
In 2025 for fiscal year 2024:
The companies* that meet at least 2 of these 3 criteria:
- More than 500 employees on average over the financial year
- More than €25 M balance sheet
- More than €50 million in sales
groups (consolidating companies)* that meet at least 2 of these three criteria:
- More than 250 employees on average over the financial year
- More than 30 M€ balance sheet
- More than €60 million in sales
*which are public interest entities, such as listed companies, credit institutions, mutual societies, …(defined in article L 821-2 of the French Commercial Code).
In 2026 for fiscal year 2025 :
All companies that meet at least 2 of these 3 criteria:
More than 250 employees on average over the financial year:
- Over €25 million in assets
- Over €50m in sales
In 2027 for fiscal year 2026 :
Listed SMEs.
In 2028 for the 2027 financial year:
Large non-European companies generating more than EUR 150 million in sales in the EU / subsidiary in the European Union.
The European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) has also launched a voluntary publication initiative for SMEs not subject to regulation. a voluntary publication initiative.
The CSRD specifies the need to develop sustainability standards to be applied in Europe : the ESRS (European Sustainability Reporting Standards) adopted by the European Commission on July 31, 2023 provide information requirements in terms of ” functional ” content (12 standards : ESRS1, etc…) and axes (governance, strategy, impacts, risk and opportunity management, metrics and targets).
After a double materiality analysis, the company publishes its information in narrative, semi-narrative or quantitative format, from among the more than 1,200 data points listed.
To meet this regulatory need for standards-based reporting, SAP offers SAP Sustainability Control Tower (SCT). SCT can already meet the need for publication according to GRI (Global Reporting Initiative), TCFD (US), European Taxonomy (EU), WEF (World Economic Forum) standards, and for CSRD on part of the indicators, with the next ones planned on the roadmap.
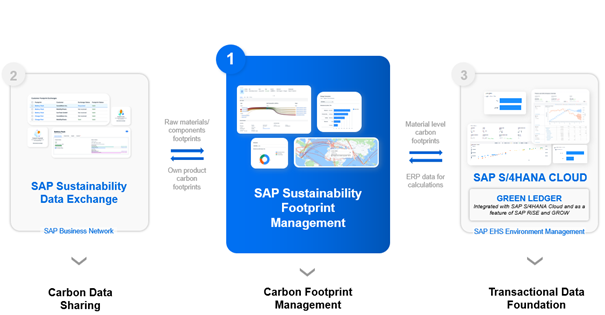
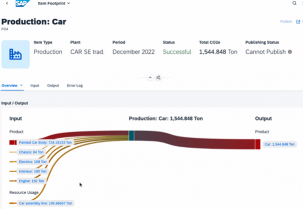
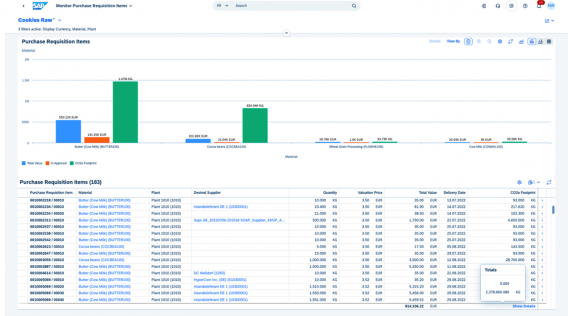
Calculating footprints with SAP Sustainability Footprint Management (SFM):
Sustainability is a top priority for managers, and accurate carbon accounting is essential to effectively combat climate change. SAP Sustainability Data Exchange enables the standardized exchange of sustainability data. Green Ledger in SAP S/4HANA CLOUD enables sustainability data to be stored at the heart of ERP processes.
Transactional carbon accounting enables more precise and granular tracking of emissions across all operations carried out by the company.
Unlike other products on the market for calculating a carbon footprint, SAP’s competitive advantage Sustainability Footprint Management (SFM) is integration with ERP upstream and downstream of the calculation flow :
Calculating production-related data and impacts with SAP Responsible Design & Production
In our current economy, we take materials from the Earth, make products from them and end up throwing them away as waste – the process is linear (“Take / Make / Waste”). In a circular economy, the model advocated by the Ellen McArthur Foundation, we slow down the production of waste thanks to three design-led principles (“Eliminate / Circulate / Regenerate”):
SAP Responsible Design and Production (RDP) is part of the circular economy and addresses Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR):
- 91% of citizens and consumers are concerned about plastic waste – source UNEP
- 73% of consumers are willing to pay more for eco-responsible packaging – source trivium packaging
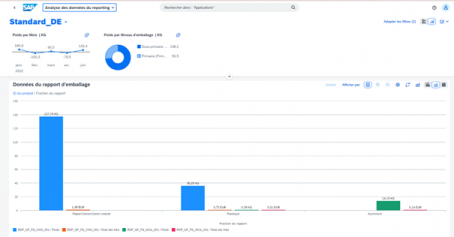
EPR contributions are calculated differently in different countries. SAP Responsible Design & Production is SAP’s solution for companies that have to draw up a CITEO declaration in France.
In addition, this solution can also be used for other countries that have to calculate plastic taxes, such as the UK and Spain.
RDP makes it possible to track corporate eco-design commitments according to the proposals of the Ellen McArthur Foundation or to adopt the SPHERE framework proposed by the WBCSD in order to eliminate unnecessary costs and waste.
The RDP solution:
- Collection of data on production, recipes, batches, logistics, materials used and sales
- Audits volumes of material types, assesses impact indicators
- Makes measurements and manages EPR declaration forms, fees, payments, plastic taxes
- Provides information for financial reporting, sustainability reporting, investors and audits
- Rethinks products and packaging to make them more sustainable
- Provides detailed design screens for product managers, product designers and packaging designers
- Holistic packaging and regulatory risk management for global markets : Supporting the transition to a sustainable product portfolio
- Cost reduction: Accurate calculation of fees and taxes, and implementation of measures to reduce regulatory risks
- Keeping commitments: Identifying the right trade-offs and helping to decide on a strategic portfolio of products in the circular economy
- Empowered consumers : Transitioning to a circular economy-aware product portfolio and increasing consumer engagement through zero waste commitments.
- More sustainable products : Helping to redesign products and packaging by assessing the design impact of using new materials.